
The vestibulocochlear nerve is derived from the embryonic otic placode. Hair cells of the maculae in the utricle activate afferent receptors in response to linear acceleration, while hair cells of the maculae in the saccule respond to vertically directed linear force. The other two sensory organs supplied by the vestibular neurons are the maculae of the saccule and utricle. Hair cells of the cristae activate afferent receptors in response to rotational acceleration. Three of these are the cristae located in the ampullae of the semicircular canals. The vestibular ganglion houses the cell bodies of the bipolar neurons and extends processes to five sensory organs. The vestibular nerve travels from the vestibular system of the inner ear. The exact mechanism by which sound is transmitted by the neurons of the cochlear nerve is uncertain the two competing theories are place theory and temporal theory. It is the inner hair cells of the organ of Corti that are responsible for activation of afferent receptors in response to pressure waves reaching the basilar membrane through the transduction of sound. Processes from the organ of Corti conduct afferent transmission to the spiral ganglia. The cochlear nerve travels away from the cochlea of the inner ear where it starts as the spiral ganglia. The vestibulocochlear nerve is accompanied by the labyrinthine artery, which usually branches off from the anterior inferior cerebellar artery at the cerebellopontine angle, and then goes with the 7th nerve through the internal acoustic meatus to the internal ear. This junction between the pons, medulla, and cerebellum that contains the 8th nerve is called the cerebellopontine angle.

The 8th cranial nerve runs between the base of the pons and medulla oblongata (the lower portion of the brainstem).
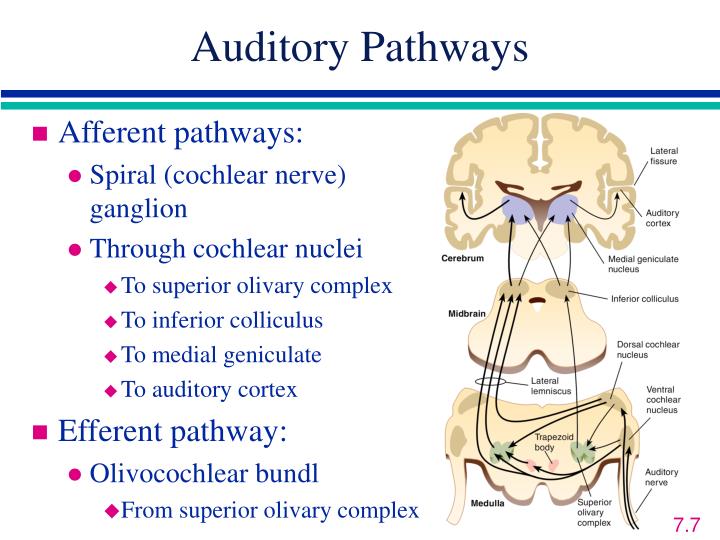
The vestibulocochlear nerve consists mostly of bipolar neurons and splits into two large divisions: the cochlear nerve and the vestibular nerve.Ĭranial nerve 8, the vestibulocochlear nerve, goes to the middle portion of the brainstem called the pons (which then is largely composed of fibers going to the cerebellum). Through olivocochlear fibers, it also transmits motor and modulatory information from the superior olivary complex in the brainstem to the cochlea. The vestibulocochlear nerve or auditory vestibular nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VIII, or simply CN VIII, is a cranial nerve that transmits sound and equilibrium (balance) information from the inner ear to the brain.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
